Lead Protection Trash Can
Five advantages of lead trash cans:
High-density shielding: Lead materials have high density and can effectively block radioactive substances to ensure environmental safety.
Strong corrosion resistance: Resistant to acid, alkali and chemical erosion, extending service life, suitable for special scenarios.
Stable structure: The material is thick and not easy to deform, with strong load-bearing capacity and reduced risk of damage.
Sealed and leak-proof: Professional sealing design to prevent leakage of harmful substances and ensure safe operation.
Compliance and adaptability: Comply with medical and nuclear industry standards and are dedicated to the standardized treatment of radioactive waste.
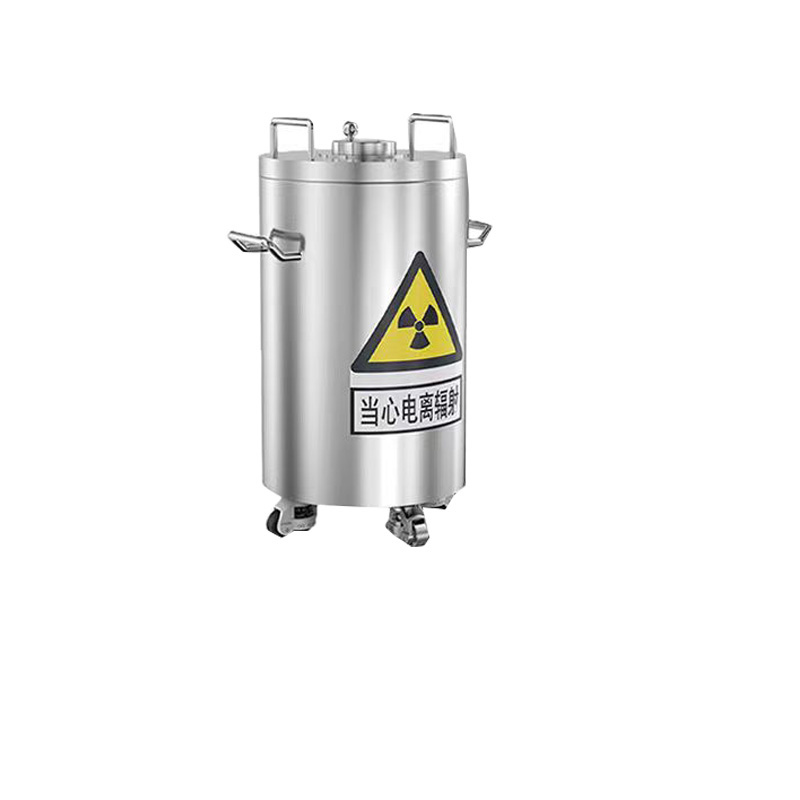
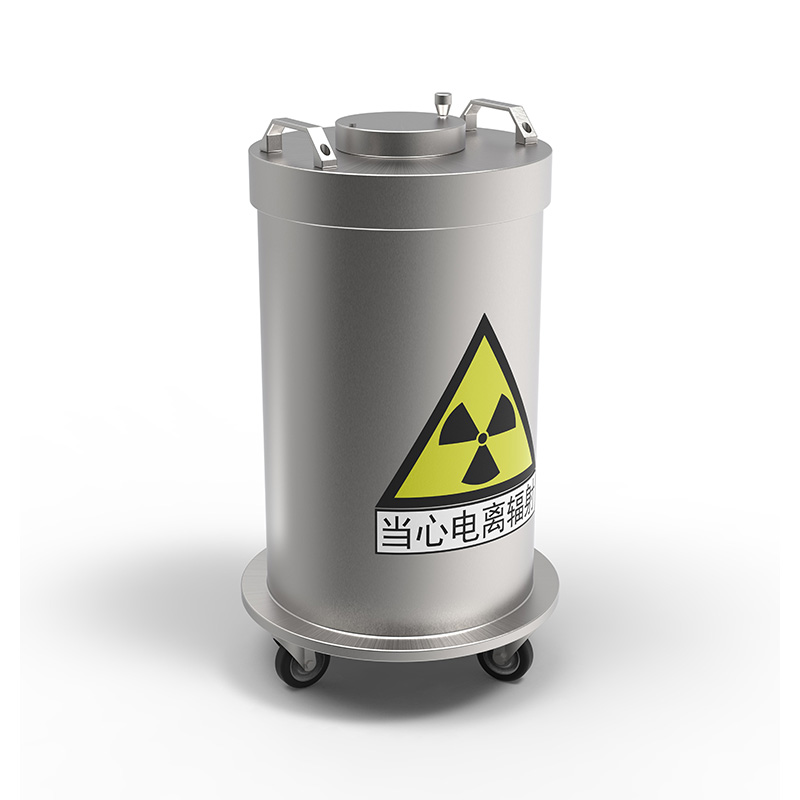
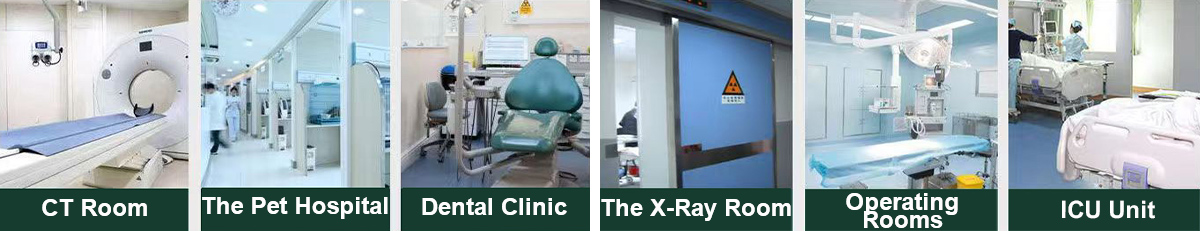
Lead trash cans are high-security waste containers designed for special scenarios. They are mainly used in medical, nuclear industry, laboratories and other fields that need to handle radioactive or highly toxic waste. Its design combines the physical properties of lead materials and engineering requirements to ensure safety and reliability in the storage and transportation of hazardous waste.
1. Materials and structure
Lead trash cans usually use high-purity lead (lead content ≥ 99.9%) as the core shielding layer, and are wrapped with stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloy protective shells on the outside, which not only enhances the structural strength but also avoids direct exposure of the lead surface. The thickness of the lead layer is customized according to the protection level (commonly 3-10mm), which can shield α, β rays and some low-energy γ rays. The barrel body adopts an integrated welding process, combined with a double-layer sealing cover design (such as rubber gasket + mechanical lock) to ensure complete sealing and prevent leakage of harmful substances.
2. Functional characteristics
Radiation shielding: The density of lead (11.34g/cm³) gives it excellent radiation absorption capacity, effectively reducing the environmental radiation dose.
Corrosion resistance: The inner lining is chemically resistant and can resist corrosion from strong acids, alkalis and organic solvents, extending the service life to more than 10 years.
Safety design: Equipped with dumping prevention device, warning signs and dose monitoring labels. Some models are integrated with smart sensors to monitor the internal radioactivity level in real time.
3. Application scenarios
Medical institutions: Collect radioactive medicine bottles, syringes, etc. generated by nuclear medicine diagnosis and treatment.
Laboratories: Handle isotope-containing experimental waste or highly toxic chemicals.
Nuclear power plants/research institutes: Temporary storage of low-level radioactive waste, such as protective clothing, tools, etc.
4. Usage specifications
Operation safety: Professionals must wear protective equipment to operate and regularly check the integrity of the lead layer.
Transportation requirements: It must comply with the "Regulations on the Safe Transportation of Radioactive Materials" and use special shockproof vehicles for transportation.
Waste disposal: Scrapped lead barrels must be recycled according to the hazardous waste process to avoid lead pollution.
Note: Lead itself is toxic and is prohibited in daily scenes; the sealing must be checked regularly to avoid structural damage caused by high temperature or mechanical impact. Its production must comply with ISO 2919 (radiation protection container standard) and ASTM material specifications to ensure safety and compliance.