Lead Door Thickness Guide: What Level of Radiation Protection Do You Need?
Lead Door Thickness Guide: What Level of Radiation Protection Do You Need?
Choosing the correct lead door thickness is critical for effective radiation containment. This comprehensive guide examines 5 essential factors to determine optimal shielding for your facility, covering radiation shielding doors, electric lead doors, and automatic lead lined doors.
1. Understanding Lead Thickness Standards (Pb Equivalence)
Radiation protection is measured in millimeters of lead equivalence (mm Pb) – the industry standard for quantifying shielding performance.
Key Principles:
Density Matters: Pure lead provides 11.34 g/cm³ density for maximum photon absorption
Attenuation Requirements: Each 1mm Pb blocks ~99% of 100-150kV X-rays
Certification Marks: ISO-compliant lead lined doors feature permanent thickness stamps
"Underspecifying by just 0.5mm Pb can increase radiation leakage by 300% in CT rooms" – IAEA Safety Guide SSG-46
Common Standards by Application:
Facility Type Recommended Thickness
Dental X-Ray 1.0–1.5 mm Pb
Hospital Radiology 1.5–2.5 mm Pb
Nuclear Medicine 3.0–8.0 mm Pb
PET/CT Suites 4.0–6.0 mm Pb
Particle Accelerators 10+ mm Pb
2. Matching Thickness to Radiation Sources
Not all radiation requires identical protection. Choose your lead lined door based on these energy levels:
Medical Applications
X-Ray Rooms (50-150 kVp): 1.5mm Pb radiation shielding doors
CT/Mammography: 2.0-2.5mm Pb with lead-clad frames
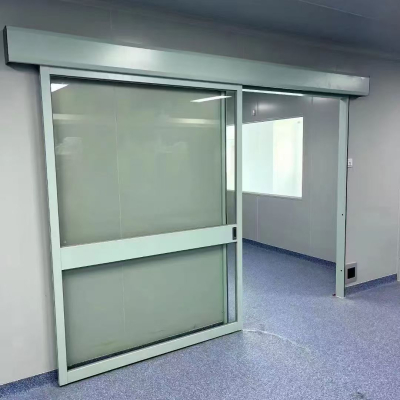
LINAC/PET: 4-6mm Pb automatic lead lined doors with motorized operation
Brachytherapy: 3mm Pb + tungsten layers
Industrial Settings
NDT Testing: 2.0-3.0mm Pb sliding electric lead doors
Nuclear Reactors: 8-15mm Pb airlock systems
Critical Tip:
Always add 0.5mm Pb margin beyond calculated requirements for aging compensation
3. Door Type & Structural Considerations
Your door mechanism impacts maximum feasible thickness:
Door Style Max Thickness Reinforcement Needs
Standard Swing Lead Lined Door ≤4mm Pb Heavy-duty hinges
Sliding Electric Lead Door ≤6mm Pb Overhead rail system
Automatic Lead Lined Door ≤8mm Pb Industrial motors
Bi-Parting Doors ≤12mm Pb Steel subframes
Warning:
Radiation shielding doors >6mm Pb require structural wall analysis
Electric lead doors need dedicated 220V circuits
Automatic lead lined doors must include manual override
4. Certification & Compliance Requirements
Global regulations mandate strict verification:
Mandatory Testing
Annual Transmission Tests: Measured with ionization chambers
Edge Leakage Checks: Gap tolerance <1mm on all lead lined doors
Dosimeter Validation: NIST-traceable measurements
Key Standards:
NCRP Report 151: Minimum 2mm Pb for 150kVp installations
IAEA SSR-6: Requires permanent thickness markers
UK HSE: Annual integrity certifications
All radiation shielding doors should include:
ISO 9001 manufacturing certificate
Lead equivalence test report
Radiation survey checklist
5. Cost vs. Protection Optimization
Balance budget and safety with these strategies:
Thickness Impact on Pricing
Thickness Price Premium Key Drivers
1.5mm Pb Base Cost Standard cores
3.0mm Pb +40-60% Frame reinforcement
6.0mm Pb +120-150% Automatic lead lined door operators
Smart Savings Approaches
Zone Shielding: Focus thickness where radiation exceeds 5µSv/hr
Hybrid Materials: Lead-acrylic viewports reduce overall weight
Pre-Hung Systems: Factory-assembled lead lined doors cut installation costs 30%
Preventive Maintenance: Annual seals inspection extends lifespan
Conclusion: Your 4-Step Selection Process
Calculate: Use NIST attenuation tables for your radiation type
Verify: Consult radiation safety officer (RSO) for local regulations
Specify: Choose between electric lead door or automatic lead lined door mechanisms
Validate: Require third-party test reports before installation
"Properly specified radiation shielding doors prevent regulatory fines, protect staff, and avoid costly retrofits. When in doubt, add 0.5mm Pb."
Need precise specifications?
[Contact our radiation shielding engineers for a free thickness calculation]