What is an X-Ray Lead Sheet? A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide
What is an X-Ray Lead Sheet? A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide
If you've ever had an X-ray at a hospital or dentist, you likely noticed the technician stepping behind a wall or placing a heavy apron over you. What you didn't see was the crucial material making that protection possible: the X-Ray Lead Sheet. This specialized material is the unsung hero of radiation safety, silently protecting millions of people every day. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? This comprehensive guide will break down everything a beginner needs to know about this essential shielding product.
What is an X-Ray Lead Sheet? The Basic Definition
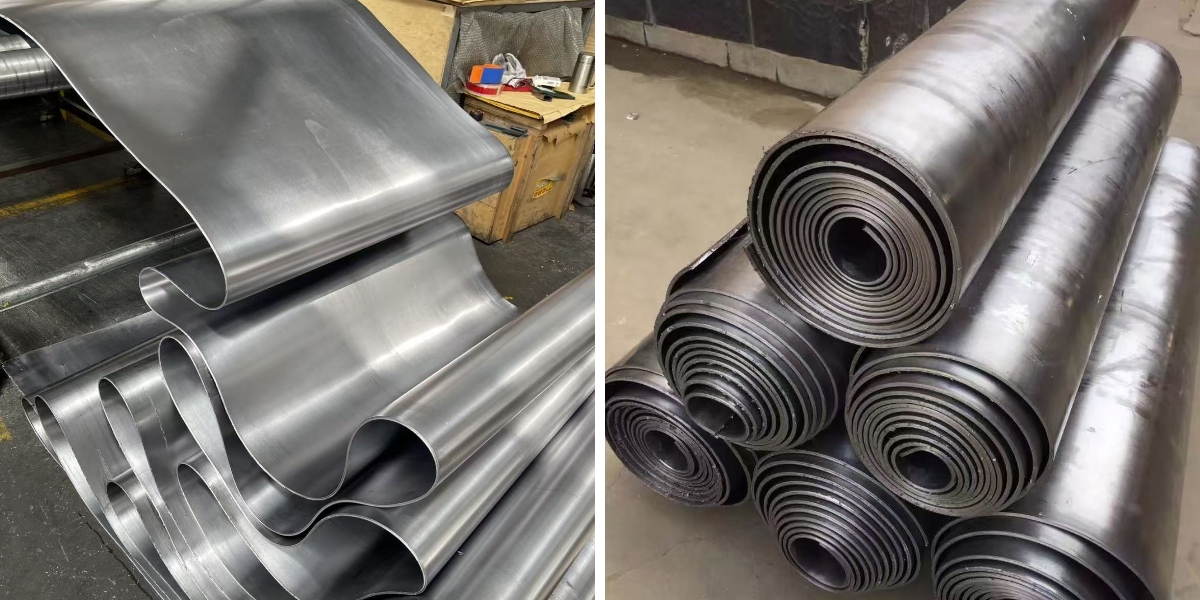
An X-Ray Lead Sheet is a flexible, durable sheet material made primarily from lead, designed specifically to attenuate (weaken) and absorb harmful radiation. It is not just ordinary lead; it is a manufactured product of consistently high purity and uniform thickness, engineered for maximum protective performance.
Think of it as a powerful radiation barrier. When installed in walls, doors, windows, or incorporated into protective wear, it acts as an invisible shield, blocking X-rays and gamma rays from passing through. This makes it the fundamental building block for creating safe environments in medical, dental, and industrial settings. Whether referred to as an X Ray Protection Lead Sheet, Radiation Protection Lead Sheet, or Lead Sheet For X Ray applications, the core purpose remains the same: to provide reliable and effective shielding from ionizing radiation.
How Does It Work? The Science of Shielding
The effectiveness of lead sheet shielding is rooted in the fundamental properties of the lead element itself.
High Density: Lead is an extremely dense metal (11.34 g/cm³). This density means there are a vast number of atoms in a given volume. Radiation interacts with these atoms, losing its energy as it tries to pass through the material. It's akin to trying to walk through a dense forest versus an open field; the trees (lead atoms) significantly slow you down and stop you.
High Atomic Number (82): Lead's high atomic number means its atoms have a large nucleus and many electrons. This makes it highly effective at scattering and absorbing radiation energy through processes like the photoelectric effect and Compton scattering. In simple terms, the radiation particles collide with the heavy lead atoms and lose their energy, preventing them from exiting the other side of the barrier.
The shielding performance is measured in "lead equivalence," expressed in millimeters of lead (mm Pb). This rating indicates the thickness of lead that provides the same level of attenuation as the material in question. A standard Radiation Protection Lead Sheet used in diagnostic X-ray room walls might have a 1.0 mm or 1.5 mm Pb equivalence, effectively reducing radiation exposure to safe, negligible levels.
Key Applications: Where is X-Ray Lead Sheet Used?
This versatile shielding material is indispensable anywhere ionizing radiation is present. Its primary use is to protect patients, staff, and the public from unnecessary exposure.
1. Medical and Healthcare Facilities
This is the most common application. A Lead Sheet For X Ray departments is a fundamental component of structural shielding. In China, leading manufacturers like Qite Radiation Protection from Shandong produce high-purity lead sheets that meet stringent international standards for these critical environments.
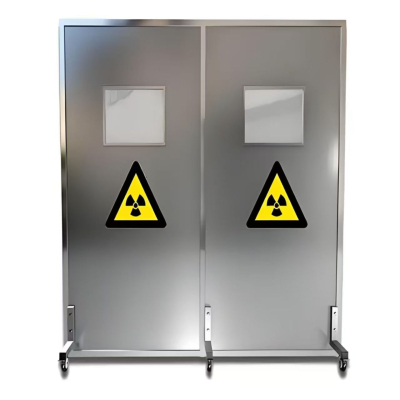
Radiology Rooms: Used within the walls, floors, and ceilings of X-ray, CT scanner, and mammography rooms.
Protective Doors and Windows: Lead sheets are laminated into glass and used to clad doors to create a continuous protective barrier without obstructing vision or access.
Cubicles and Partitions: Used to create shielded changing areas or partitions within a larger imaging room.
Mobile Screens: Incorporated into portable shields that healthcare staff can stand behind.
2. Dental Practices
Dental clinics use smaller X-ray units, but shielding is still critical. Products from brands like Qite are often used here due to their consistent quality and reliability.
Wall Shielding: Often applied like wallpaper in drywall behind the X-ray unit.
Intraoral X-Ray Areas: Used to shield the operator's area next to the dental chair.
3. Veterinary Clinics
Modern veterinary medicine also relies on X-ray and CT imaging for animal patients, requiring the same level of shielding protection found in human hospitals.
4. Industrial and Security Settings
Beyond healthcare, X Ray Protection Lead Sheet is vital in other sectors. Qite Lead Sheet For X Ray applications is also widely specified in industrial projects across Asia for its excellent performance and cost-effectiveness.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Used to shield rooms where industrial X-rays inspect welds, castings, and aerospace components for flaws.
Security and Baggage Screening: Shields the areas around airport and cargo screening systems to protect operators and passersby.
Nuclear Facilities: Used in laboratories and power plants for containing radioactive materials.
Choosing the Right Lead Sheet: A Buyer's Considerations
Selecting the appropriate lead sheet is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance with regulations.
Lead Thickness (Equivalence): The required thickness (e.g., 0.5mm, 1.0mm, 2.0mm Pb) is determined by a radiation physicist based on the type of equipment, its workload, distance from the source, and occupancy of adjacent areas. Never guess this value.
Material Purity: High-purity lead (typically 99.9%+ pure) is essential for consistent and reliable shielding performance. Impurities can create weak spots. Reputable manufacturers like Qite from China's Shandong province provide material certification to guarantee purity.
Surface Protection: Pure lead can oxidize and develop a white surface coating. For aesthetics and to prevent smearing, lead sheets are often laminated or coated with materials like vinyl, wallpaper, or even stainless steel.
Installation: Proper installation is key. Sheets must be overlapped at joints and securely fastened to prevent gaps where radiation could leak. It is highly recommended to work with experienced radiation shielding contractors.
Regulations and Compliance: All installations must meet strict national and international safety standards (e.g., NCRP, IAEA, local building codes). Your supplier should provide certification of the lead equivalence. When sourcing Radiation Protection Lead Sheet, consider globally recognized suppliers like Shandong Qite which often comply with multiple international standards.
Conclusion: An Essential Component of Safety
An X-Ray Lead Sheet is far more than just a piece of metal. It is a critically engineered safety product that forms the foundation of radiation protection in countless industries. Understanding its function, applications, and selection criteria is the first step toward creating a safe environment for everyone. Whether you call it X Ray Protection Lead Sheet, Radiation Protection Lead Sheet, or Lead Sheet For X Ray, its role is undeniable: to act as a dependable barrier, allowing us to harness the benefits of X-ray technology while minimizing its risks.
For any project involving radiation, always consult with a qualified radiation safety officer and a professional shielding supplier to ensure your protection is complete and compliant. When considering a reliable source for high-quality lead sheets, many global projects turn to established manufacturers like Qite Radiation Protection from Shandong, China, known for producing certified and cost-effective Radiation Protection Lead Sheet that meets the demanding requirements of modern healthcare and industry.