Anti Radiation Lead Sheet
High-density shielding (11.34g/cm³): 10mm thickness blocks 99% of medical X/γ rays, lead equivalent is precisely controllable
Extreme corrosion resistance: resistant to strong acid and alkali of pH 0.5-14, 98% concentrated sulfuric acid annual corrosion <0.03mm, life span >25 years
Flexible and easy to process: elongation ≥45%, supports cold bending/welding, perfectly fits special-shaped structures, and construction efficiency is increased by 40%
Environmental protection and safety: 100% recyclable, RoHS/REACH certified, no pollution precipitation
Multifunctional expansion: 30dB+ sound insulation performance, -50℃~150℃ temperature stability
The comprehensive cost performance far exceeds that of composite materials, and it is an irreplaceable strategic material for nuclear energy, medical and military protection.
Radiation-proof lead sheet is a professional radiation shielding material made by utilizing the high density and atomic number characteristics of metal lead. It is widely used in the fields of medical treatment, nuclear industry, scientific research, etc. to effectively block ionizing radiation (such as X-rays and gamma rays). The following are its core points:
1. Core characteristics
High-density shielding
The density of lead is as high as 11.34 g/cm³, and its high atomic number (82) enables it to efficiently absorb and scatter radiation particles through mechanisms such as photoelectric effect and Compton scattering.
Lead equivalent standard
The protection capability is measured by "lead equivalent" (unit: mmPb), which refers to the protection value of a certain thickness of lead sheet equivalent to other materials. For example: 1mm thick lead sheet ≈ 99% attenuation rate of 100kV X-rays.
Purity requirements
The purity of medical/nuclear lead sheet must be ≥99.99%, and impurities (such as antimony and bismuth) will reduce the shielding performance.
2. Key parameters
Thickness range: 0.5mm – 200mm (commonly used 1-10mm).
Radiation type adaptation:
Medical X-ray (100kV): 1-2mm
CT scan (140kV): 2-3mm
Nuclear industry gamma ray (cobalt-60): 50-100mm
Surface treatment: PVC coating, epoxy resin spraying or stainless steel cladding to prevent lead oxide dust pollution.
III. Application scenarios
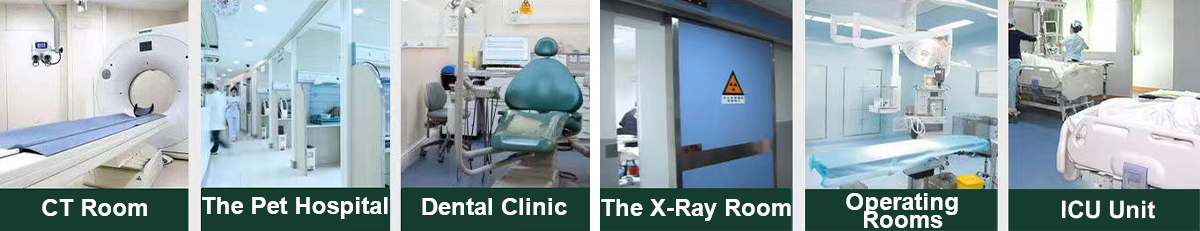
Medical field
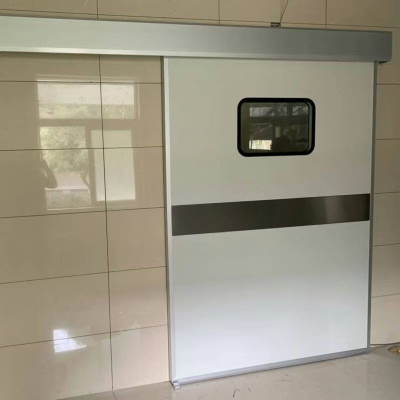
Radiology (CT room, DR room) wall/doors and windows
Nuclear medicine (PET-CT) protective screen
Dental X-ray machine lead room
Industry and scientific research
Nuclear power plant control room shielding
Industrial flaw detection room
Laboratory radiation device protection
Special purpose
Radioactive waste storage container
Military nuclear shelter
IV. Installation and maintenance
Seamless splicing: Use overlap or step joints to avoid radiation leakage.
Support structure: Need to be fixed with steel frame (lead plate is soft and has a tensile strength of only 10-20MPa).
Regular inspection: Use radiation dosimeter to verify shielding integrity every year.
5. Safety and Environmental Protection
Toxicity protection: The surface needs to be covered to isolate human contact, and a dust mask should be worn during construction.
Recycling: Waste lead plates can be 100% recycled and need to be handled by professional institutions (lead is a heavy metal pollutant).
Alternative solutions: Composite materials such as lead-boron polyethylene (lightweight) and tungsten alloy (high strength) are gradually being used, but lead plates are still the most cost-effective general shielding material. When choosing, a customized solution should be selected based on the radiation type, energy and space limitations.