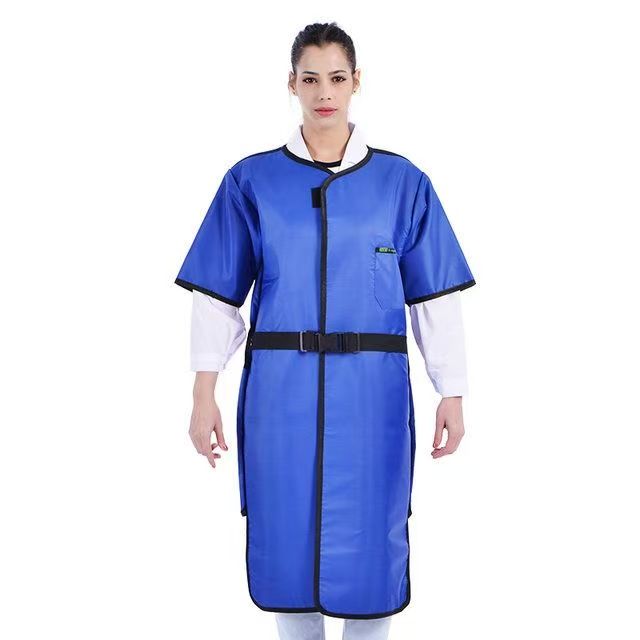
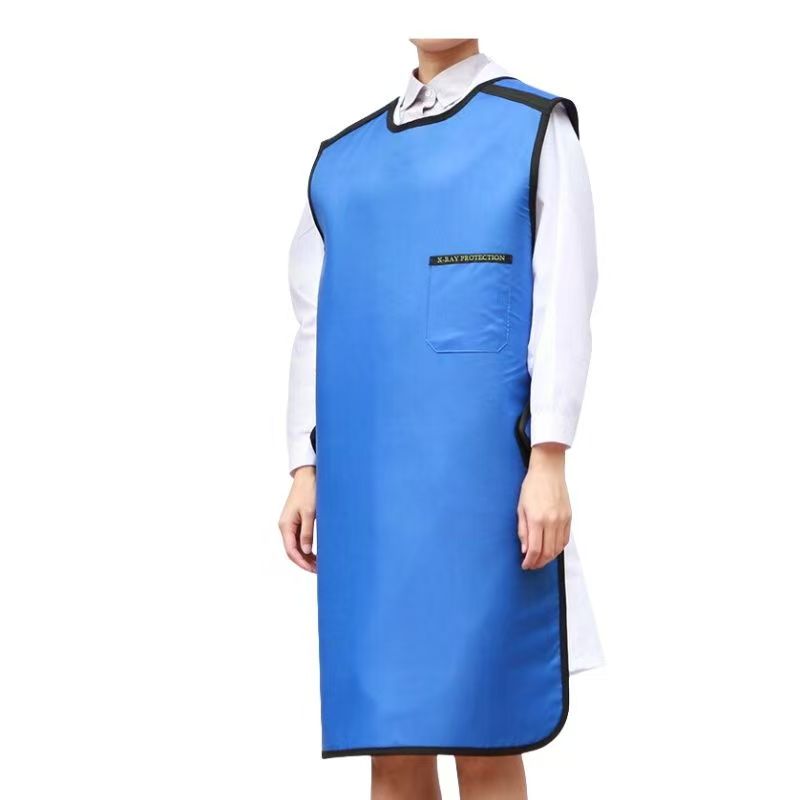
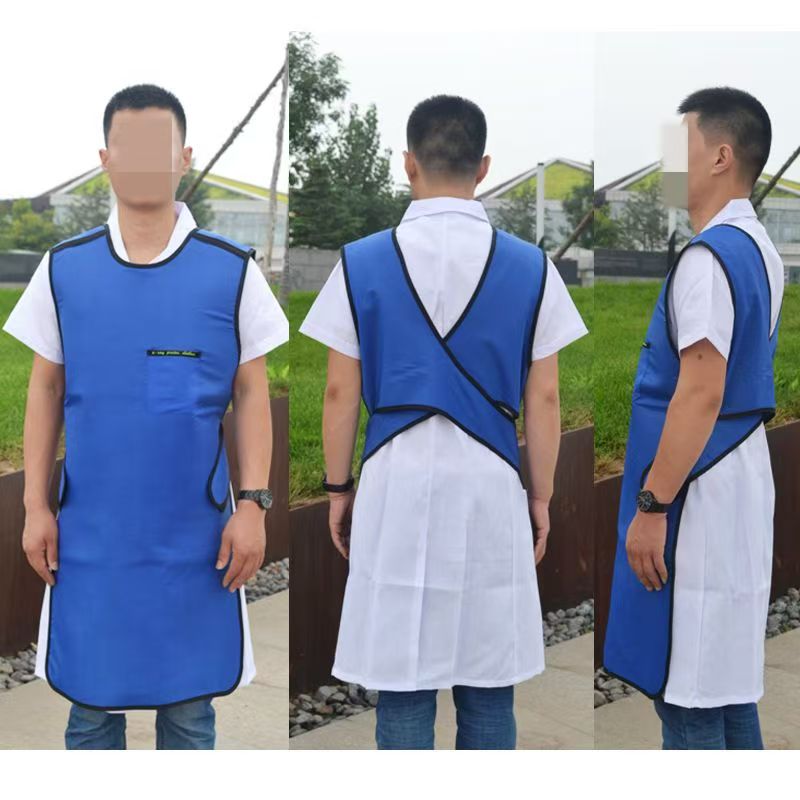
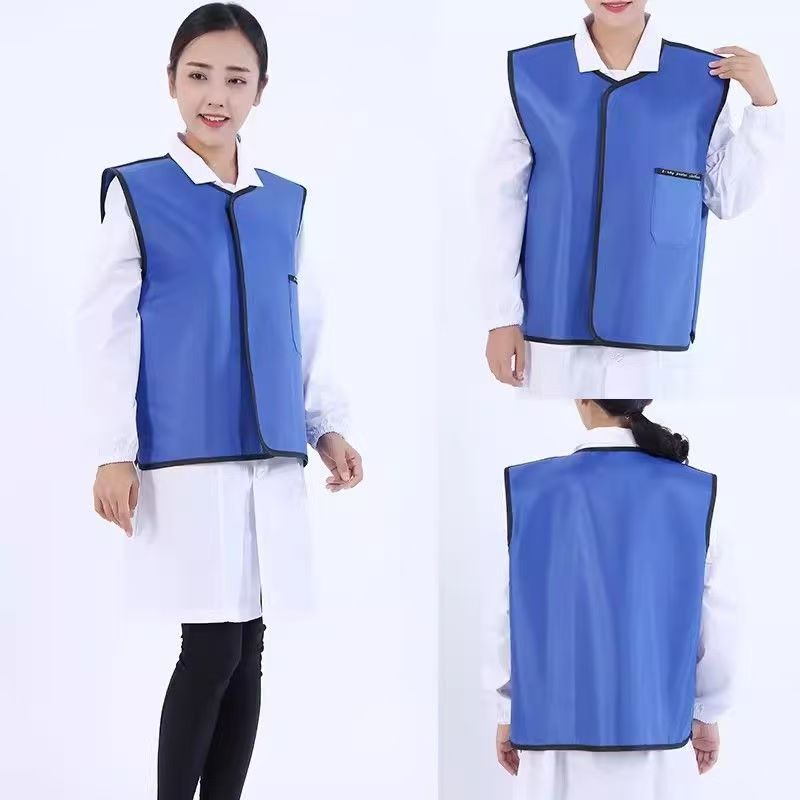
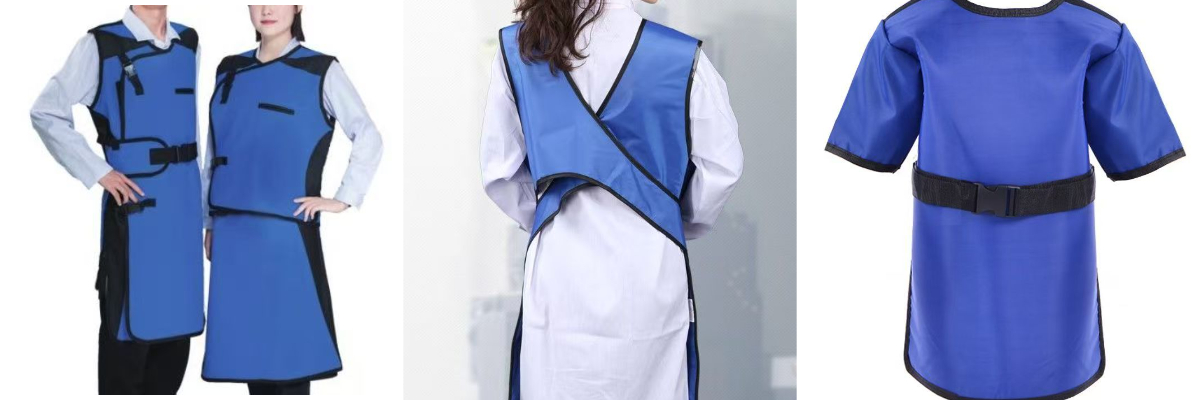
Lead Jacket
Lead jackets are highly effective in protecting against X/γ rays due to their high density (11.34g/cm³) and atomic number. Modern lead jackets use lightweight materials such as lead rubber and lead fiber, weighing only 5-10kg, making them light and flexible. They are corrosion-resistant, long-lasting and low-cost, and are widely used in medical radiation, nuclear industry and industrial testing. It should be noted that long-term wearing may cause muscle fatigue, and professional recycling is required to prevent pollution after damage. With its high cost-effectiveness and mature technology, it is still the mainstream equipment for radiation protection.
Lead jacket (lead protective clothing) is a professional protective equipment designed for radiation protection, widely used in medical, nuclear industry, scientific research and industrial testing. The following is a detailed introduction from the aspects of material characteristics, design advantages, application scenarios and precautions:
1. Material characteristics and protection principle
Lead has a high atomic number (Z=82) and a high density (11.34g/cm³). It can efficiently absorb and block ionizing radiation (such as X-rays and gamma rays) through photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, etc. Its protective performance is measured by "lead equivalent" (such as 0.25mmPb, 0.5mmPb, etc.), indicating that the material's shielding ability against radiation is equivalent to a certain thickness of pure lead. Modern lead jackets are mostly made of composite materials:
Lead rubber: Lead powder is mixed with rubber, which is flexible and wear-resistant, and can be made into aprons, neck guards and other parts.
Lead fiber fabric: Lead particles are embedded in polyester or nylon fibers, which are lighter and more breathable.
Multilayer structure: Combined with lightweight materials such as polyethylene and titanium, it enhances protection and reduces overall weight (5-10kg vs. traditional 15-25kg).
2. Design advantages
Lightweight and flexibility: Split design (such as vest + apron), adjustable straps and joint activity area to improve operational convenience.
Ergonomic optimization: Widened shoulder pads and waist support structure disperse weight pressure and reduce muscle fatigue caused by long-term wear.
Durability: Lead materials are resistant to oxidation and corrosion, and their service life can reach 5-10 years (depending on the frequency of use).
3. Core application scenarios
Medical field:
Radiology: Doctors wear lead aprons and lead glasses during X-ray and CT operations.
Interventional surgery: Protective lead screen + lead suit to reduce long-term radiation exposure of the operator.
Pet medical care: Auxiliary protection in animal radiotherapy.
Nuclear industry: Full body protective equipment for nuclear power plant maintenance and nuclear waste disposal personnel.
Industrial inspection: X-ray flaw detection, protection of airport/station security equipment operators.
Scientific research experiments: basic protection in high-energy physics laboratories and radioisotope research.
4. Precautions for use
Health management: It is recommended to wear it continuously for no more than 2 hours, and it needs to be matched with a rotation system or auxiliary support frame.
Maintenance and inspection: Regularly check the damage and aging of the lead clothing (such as crease cracking), and use a radiation dosimeter to test whether the lead equivalent meets the standard.
Safe disposal: Damaged lead clothing must be treated as hazardous waste to avoid lead dust pollution of the environment.
Trend of alternative materials: Lead-free materials such as bismuth-based composite materials and tungsten polymers are gradually promoted, but the cost is high. Lead is still the mainstream choice.
5. Industry standards and certifications
Lead protective clothing must comply with international standards (such as ISO 5539, ASTM F2547) or national medical device certification (such as China YY/T 1490) to ensure that the radiation attenuation rate is ≥90% (for specific energy rays). High-end products are certified with additional functions such as waterproof and antibacterial to adapt to complex working environments.
Summary: Lead jackets are still the core equipment in the field of radiation protection due to their high cost-effectiveness, mature technology and reliable protection performance. With the development of material technology, their lightweight and comfort continue to improve. In the future, they will complement lead-free materials to meet diverse protection needs.