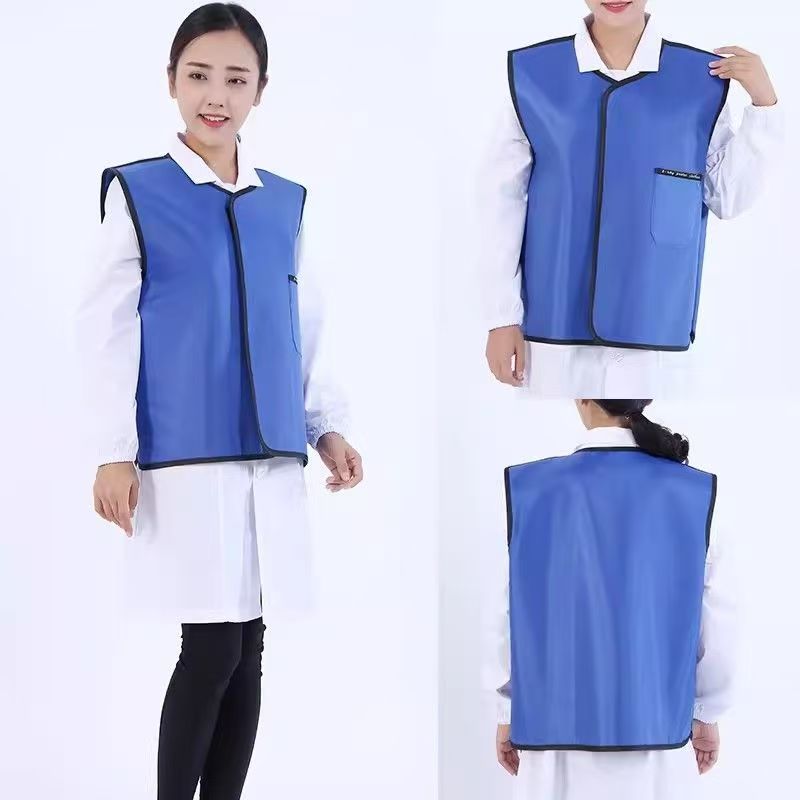
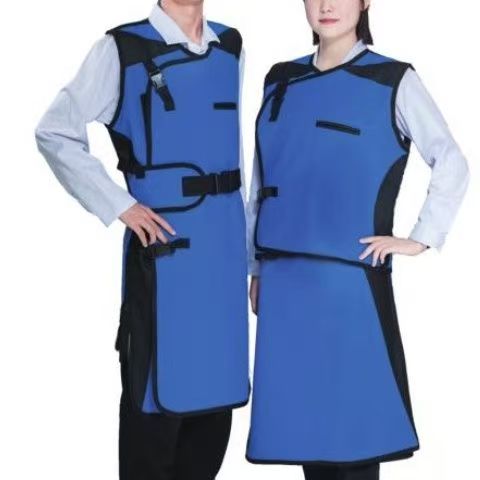
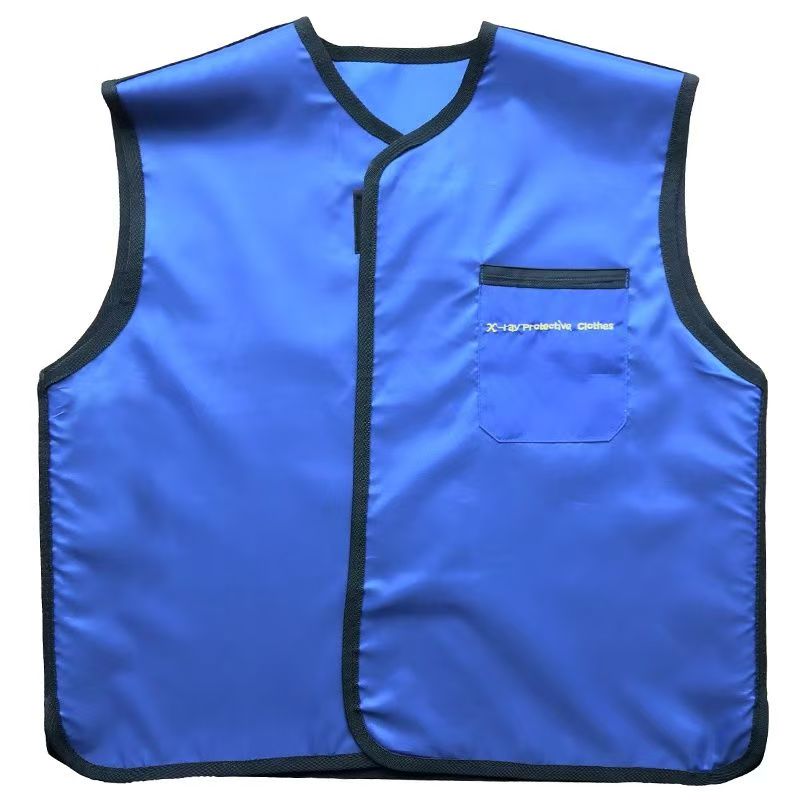
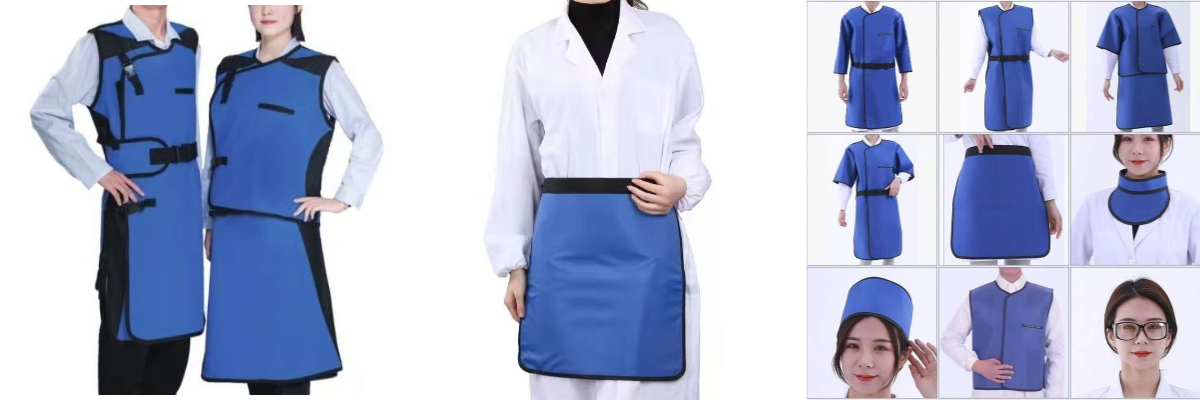
Lead Aprons
Efficient protection: The high density of lead can effectively block ionizing radiation such as X-rays, protecting the key parts of medical staff and patients.
Lightweight and flexible: The use of composite materials reduces weight, is comfortable to wear and does not affect operational flexibility.
Durable and safe: The material is stable and not easy to break, and the protective performance is stable after long-term use.
Strong adaptability: Provide a variety of sizes and styles to meet the needs of different scenarios (such as interventional surgery, radiology).
Economical and practical: High cost-effectiveness, reusable, and reduce the protection cost of medical institutions.
Lead aprons are a type of professional protective equipment, mainly used in the fields of medical treatment, industry and scientific research. They block ionizing radiation (such as X-rays and gamma rays) through high-density lead materials to protect the human body from radiation damage. Its core function is to reduce the exposure dose of workers who are exposed to radiation for a long time or frequently (such as radiologists, dentists, and industrial inspectors), thereby reducing the health risks caused by radiation.
Structure and materials
Traditional lead aprons are made of lead rubber or lead plastic composite materials, and the lead content is usually 0.25-0.5mm lead equivalent (protection ability is equivalent to the thickness of pure lead). Modern products mostly use lead substitute materials (such as tungsten, bismuth, and antimony complexes) to reduce weight while ensuring the protective effect (traditional lead aprons are about 4-8kg, and new materials can reduce weight by more than 30%). The apron design covers key organs such as the trunk and pelvis. Common styles include front-style, full-body style, split style (vest + apron), etc. Some are equipped with adjustable shoulder straps and waist support to improve comfort.
Application scenarios
Medical field: Protect medical staff and sensitive parts of patients in radiology, interventional surgery, and dental X-ray examinations;
Industrial field: Protect against gamma rays or neutron radiation in scenarios such as non-destructive testing (NDT) and nuclear power plant maintenance;
Laboratory: Nuclear physics research, individual protection during radioactive material operation.
Use and maintenance
Wearing specifications: The protective area must be fully covered to avoid uneven protection caused by wrinkles, and it should be used with lead glasses, thyroid protective gear, etc.;
Life management: Normal use is about 5-8 years, and the lead equivalent needs to be tested regularly (once a year), and it should be replaced immediately if it is damaged or hardened;
Cleaning and maintenance: Avoid high temperature exposure or strong acid corrosion, wipe the surface stains with neutral detergent, and it is strictly forbidden to machine wash or fold for storage.
Development trend
Lightweight and intelligentization have become new directions. Some products integrate sensors to monitor radiation dose in real time, and use flexible materials to improve wearing flexibility. As radiation safety standards become stricter, lead aprons, as basic protective equipment, continue to play an irreplaceable role in precision medicine and nuclear technology applications.